Understanding the Basics of AI
NOTICE
Content submitted to AI tools is not private.
CAUTION
AI tools may produce inaccurate or biased outputs, including misinformation or unintended biases related to race or gender.
What is Generative AI?
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) is a term that refers to a type of “AI algorithms that can create a variety of content types—including alphabetic text, images, and sound—based on patterns it has identified within a data set.” (Dobrin, 2023, p. 7) This allows the algorithm, once trained, to produce a wide variety of content. As of early 2023, several open-source (free to all) language models, including the well-known ChatGPT, were made available. These algorithms have been trained on vast amounts of natural language (primarily from the internet) to (essentially) learn how to create text in response to a request or other input.
Prompts & Large Language Models
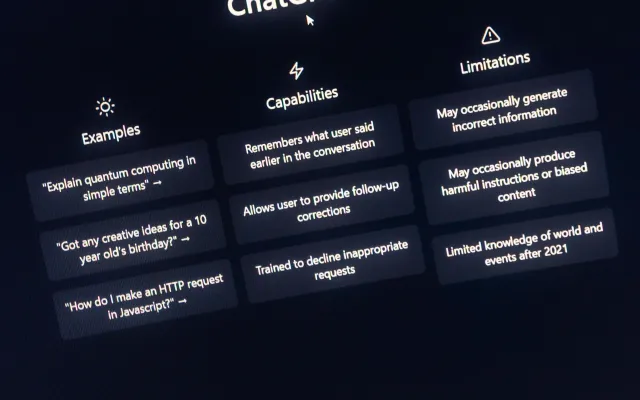
What are Prompts?
A prompt is a natural language request submitted to a language model to receive a response. Prompts can contain questions, instructions, contextual information, short examples, and partial input for the model to complete or continue. After the model receives a prompt, it can generate text, embeddings, code, images, videos, music, and more, depending on the model used.

What are Large Language Models (LLM)?
A large language model (LLM) is a computational model capable of language generation or other natural language processing tasks. For those who wish to gain a deeper understanding of LLMs, see the following resources.
- Large language models explained with a minimum of math and jargon - intermediate.
https://www.understandingai.org/p/large-language-models-explained-with
